Organic Synthesis
Rxns
| Mechanism:
|
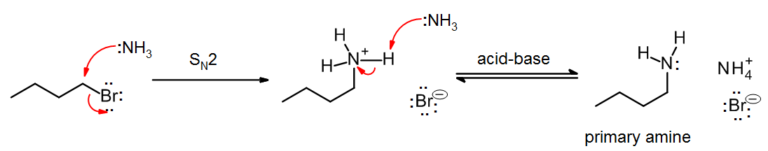 Amines and ammonia are generally sufficiently nucleophilic to undergo direct alkylation, often under mild conditions. The reactions are complicated by the tendency of the product (a primary amine, secondary, or tertiary amine) to react with the alkylating agent. For example, reaction of 1-bromooctane with ammonia yields almost equal amounts of the primary amine and the secondary amine. Therefore, for laboratory purposes, N-alkylation is often limited to the synthesis of tertiary amines. An exception is the amination of alpha-halo carboxylic acids that do permit synthesis of primary amines with ammonia. Intramolecular reactions of haloamines X-(CH2)n-NH2 give cyclic aziridines, azetidines and pyrrolidines. |
|
Return |