Organic Synthesis
Formation
Up One Mechanism: Halogenation |
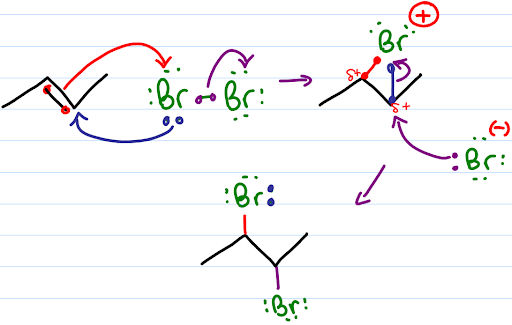 This shows the mechanism of the addition of a halogen molecule to an alkene. A halogen, for example Br2, approaches a double bond of the alkene, electrons in the double bond repel electrons in the bromine molecule causing polarization of the halogen-halogen bond. This creates a dipole moment in the halogen-halogen bond. Heterolytic bond cleavage occurs and one of the halogens obtains a positive charge and reacts as an electrophile. The reaction of the addition is not regioselective but is stereoselective. Stereochemistry of this addition can be explained by the mechanism of the reaction. In the first step, the electrophilic halogen (with the positive charge) approaches the pi bond and 2p orbitals of the halogen bond with two carbon atoms creating a cyclic ion with a halogen as the intermediate. In the second step, the remaining halide ion (halogen with the negative charge) attacks either of the two carbons in the cyclic ion from the back side of the cycle as in the SN2 reaction. Therefore stereochemistry of the product is anti addition of vicinal dihalides. |