Organic Synthesis
NamedReactions
Up One Mechanism: Freidel-Crafts-acylation |
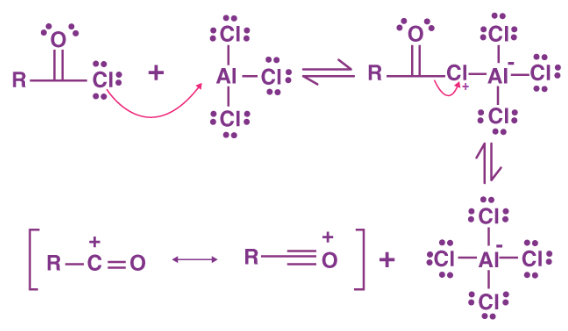 The halide of the acyl halide attacks the AlCl3. The delta positive side of the alkyl group forms a cation with the loss of the Cl to the AlCl4- and is attacked by the double bond electrons of the aromatic, bonding the alkyl carbon to the aromatic ring, and leaving a carbocation at the other side of the now missing double bond. The extra hydrogen (beside the acyl group) can be removed by a base, leaving it's electrons to reform a double bond (and the aromaticity) or the electrons can shift to the other side of the added group and do the same thing. |